About Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate, also known by popular brand names Lexan® and Makrolon®, is a thermoplastic noted for its high strength, durability and impact resistance.
It has many similar physical characteristics to acrylic, such as clarity and weight, but is much stronger and usable across a wider temperature range.
It transmits up to 90% of visible light, which makes it a popular choice as a glass substitute for machine guards, security screens, lenses and visors.
Unlike most thermoplastics, polycarbonate can be put under severe flexural stress without breaking or cracking.
Videos


View video of attempts to break Makrolon® with a brick, a prise bar and an axe.
View video of attempts to shoot a bullet through Makrolon® Hygard®.
Lexan® is a registered trademark for SABIC Innovative Plastics.
Makrolon® is a registered trademark of Bayer MaterialScience.
 Download datasheet (144Kb)
Download datasheet (144Kb)
History
1891 – Bisphenol A, the main chemical constituent of polycarbonate, is discovered by Russian chemist Aleksandr Dianin
1953 – Polycarbonate is discovered independently by H. Schnell at Bayer AG in Germany and D. W. Fox at General Electric in the US
1982 – The first audio CD made from polycarbonate is introduced to the market, quickly replacing audio tape
1992 – Car headlights made of polycarbonate become legal in Europe. They are now used in most European vehicles
Applications
As well as high strength, polycarbonate offers exceptional heat and electrical resistance, and is put to use as barrier insulation between electronic components. It is also used as a dielectric in high stability capacitors.
Other major uses include:
- Engineering and Mining: Polycarbonate is used as machine guards to protect workers from injury when operating heavy machinery. In particular, polycarbonate guards will take an enormous amount of impact from machined components or drills breaking apart during operation. Also, polycarbonate guards protect workers in the mining industry from rock falls, or from fast-moving projectile debris during blasting
- Construction: The building industry is a major consumer of polycarbonate as a replacement for glass, for sound walls, dome lights and more
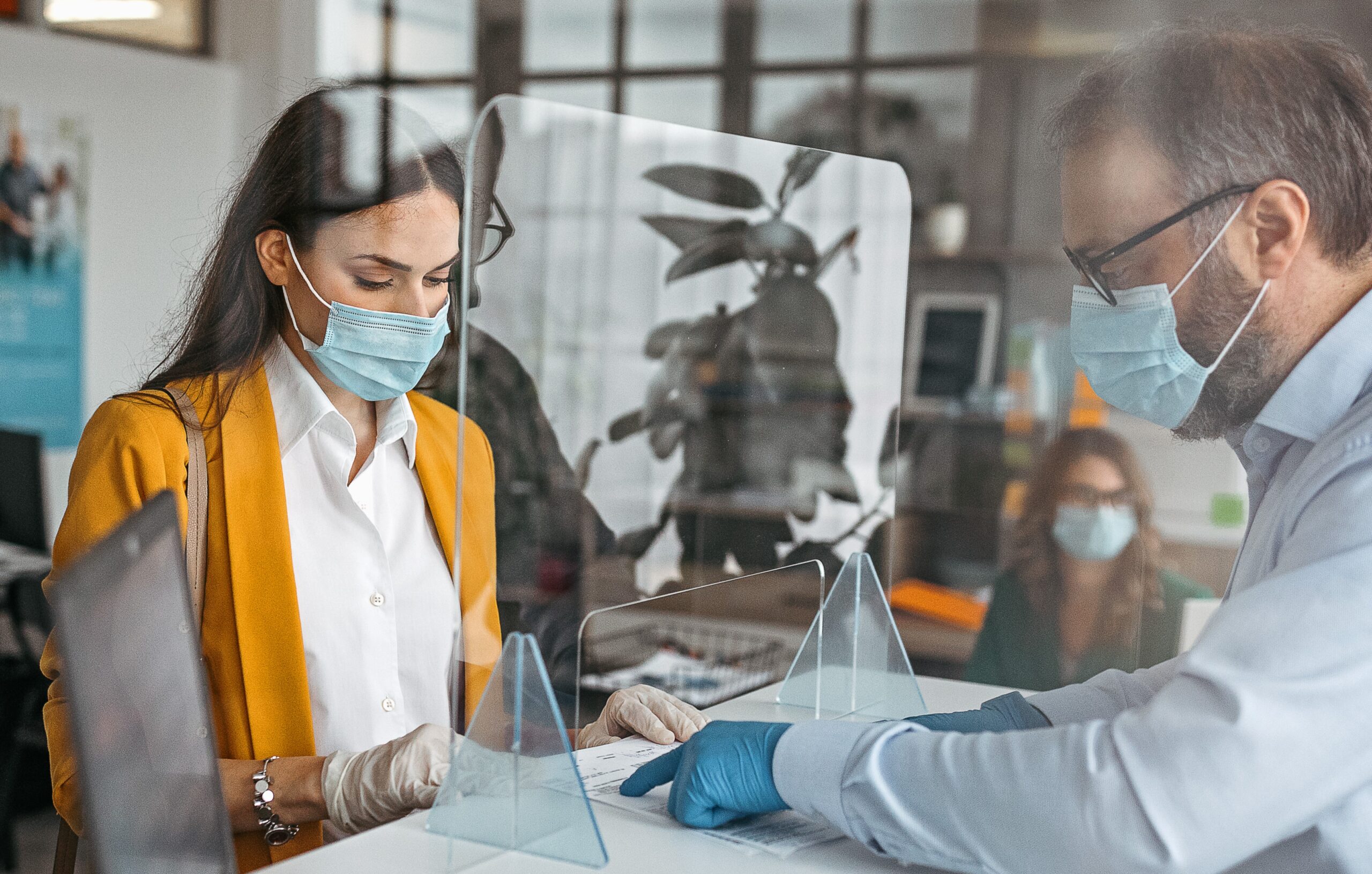
- Hospitals: Polycarbonate is used in barriers that provide security for staff and patients
- Police and Corrective Services: Its high resilience against physical attack makes polycarbonate popular for use in police stations and prison cells. The abrasion-resistant grade of polycarbonate is frequently used in these sectors
- Security: Polycarbonate is suitable for nearly any business or situation where high security or safety performance is needed, such as bank teller environments
- Data storage: Polycarbonate substrate is used in combination with an organic dye recording layer and reflective coating for CDs, DVDs and Blu-ray discs
Key Properties
General
Density relative to water (=1), 1.192
Water absorption (24 hrs), 0.02%
Thermal
Continuous Service Temperature, 120°C (248°F)
Melting point, 267°C (513°F)
Mechanical
Tensile Strength at Break, 60 Mpa
Elongation at Break, 90%
Flexural Strength, 90 Mpa
Impact Strength, Notched Izod @ 23°C, 13
![]() Download datasheet (144Kb)
Download datasheet (144Kb)